- Ras Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling and Kinase Suppressor of Ras as Therapeutic Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Hyuk Moon, Simon Weonsang Ro
-
J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):1-11. Published online March 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.1
-
-
6,330
Views
-
220
Downloads
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
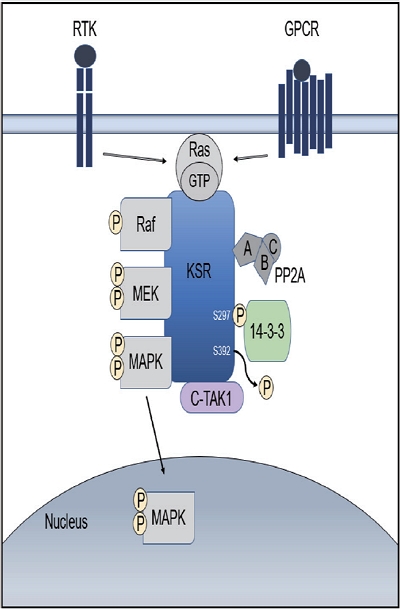
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a high incidence cancer and a major health concern worldwide. Among the many molecular signaling pathways that are dysregulated in HCC, the Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase (Ras/Raf/MAPK) signaling pathway has gained renewed attention from basic and clinical researchers. Mutations in Ras and Raf genes which are known to activate the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway have been infrequently detected in human HCC; however, the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway is activated in more than 50% of HCC cases, suggesting an alternative mechanism for the activation of the signaling pathway. Kinase suppressor of Ras acts as a molecular scaffold for facilitating the assembly of Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway components and has been implicated in the regulation of this signaling pathway. In this review, we provide important insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the activation of the Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathway and discuss potential therapeutic strategies for HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Lipid‐lowering activity and underlying mechanism of glycosylated peptide–calcium chelate prepared by transglutaminase pathway
Xiaoping Wu, Xu Chen, Xixi Cai, Shaoyun Wang
Food Frontiers.2024; 5(1): 160. CrossRef - CT-guided high dose rate brachytherapy can induce multiple systemic proteins of proliferation and angiogenesis predicting outcome in HCC
Lukas Salvermoser, Shraga Nahum Goldberg, Marianna Alunni-Fabbroni, Philipp Maximilian Kazmierczak, Moritz Nikolaus Gröper, Jan Niklas Schäfer, Elif Öcal, Tanja Burkard, Stefanie Corradini, Najib Ben Khaled, Agnese Petrera, Moritz Wildgruber, Jens Ricke,
Translational Oncology.2024; 43: 101919. CrossRef - Network-Pharmacology-Based Study on Active Phytochemicals and Molecular Mechanism of Cnidium monnieri in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Shakeel Ahmad Khan, Terence Kin Wah Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5400. CrossRef - Identification of potential target genes of honokiol in overcoming breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen
Adam Hermawan, Herwandhani Putri, Naufa Hanif, Nurul Fatimah, Heri Himawan Prasetio
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Animal Models of Liver Cancer: Current Status and Application in Preclinical Research
-
Hye-Lim Ju, Simon Weonsang Ro
-
J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):1-14. Published online March 31, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.1
-
-
3,235
Views
-
107
Downloads
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide. HCC develops
in various causes – Viral hepatitis infection, toxins, or other liver conditions - by activation of
oncogenes and/or inactivation of tumor suppressors. Understanding of signal pathways and
protein-protein interactions critical in tumor development may lead to novel treatment strategy.
To evaluate the progression of HCC and effects of potential therapies, various animal models
have been established. Experimental models of HCC provide valuable tools to investigate the
risk factors, new treatment modalities and biologic characteristics. Subcutaneous xenograft
models have been widely used in the past. However, with the advancement of in vivo imaging
technology, investigators are more concerned with the orthotopic models nowadays.
Genetically engineered mouse models have greatly facilitated studies of gene function in
HCC development. Lately, a novel approach for stable gene expression in mouse hepatocytes
by hydrodynamic injection has been developed. Each model has its own advantages and
disadvantages. Therefore, selecting the optimal models based on study objectives is necessary.
In this review, we highlight both the frequently used mouse models and some emerging ones
with emphasis on their merits or defects, and give advices for investigators to choose a ‘‘best-fit’’
animal model in HCC research.
|